Resolve Merge Conflicts
Learn how to resolve conflicts in your site code base.
Conflicts can occur when modified file(s) within your site's codebase do not align with changes made to the same file(s) in the site's upstream.
When a merge isn’t resolved automatically, Git leaves the index and the working tree in a special state that gives you all the information you need to help resolve the merge.
Resolve Conflicts When Updating Core
The fastest resolution for conflicts when updating is often to use the -Xtheirs flag. This will attempt to automatically resolve the conflicts with a preference for upstream changes.
This is safe to run if you don't have your own changes in any of the conflicting files (for example problems with .gitignore).
-
Double-check the files before going forward to make sure no bugs were introduced.
- The
-Xtheirsflag will drop your changes if you modify core CMS files. You should manually resolve conflicts in this scenario.
- The
-
Review WordPress and Drupal Core Updates for more details on core updates.
Find a Site's Upstream URL
Run the following command in Terminus to retrieve your Upstream URL:
Manually Resolve Conflicts
Steps to resolve merge conflicts vary by the type of conflict. Refer to the sections below for more information on resolving delete/modify conflicts, content conflicts, and Multidev conflicts.
Resolve Delete/Modify Conflicts
A delete/modify conflict occurs when one commit deletes a file and another modifies it. Follow the steps below to resolve such a conflict.
-
Identify the file that is generating a delete error.
For example, the Git log may contain an entry similar to the following:
-
Navigate to your local repository > run the following Git command to get a copy of the file in conflict:
Information:NoteWhen looking for a commit ID, you can find the last instance where the missing file was in the repository.
-
Run
git statusand verify that there is a new file to add to the repository:
- Stage and commit:
You will receive confirmation from Git that the file has been committed.
- Run the Git push command:
Resolve Content Conflicts
A content conflict occurs when two commits modify the same line(s) of a file non-sequentially (without one having the other in its history). For example:
Follow the steps below to resolve this scenario.
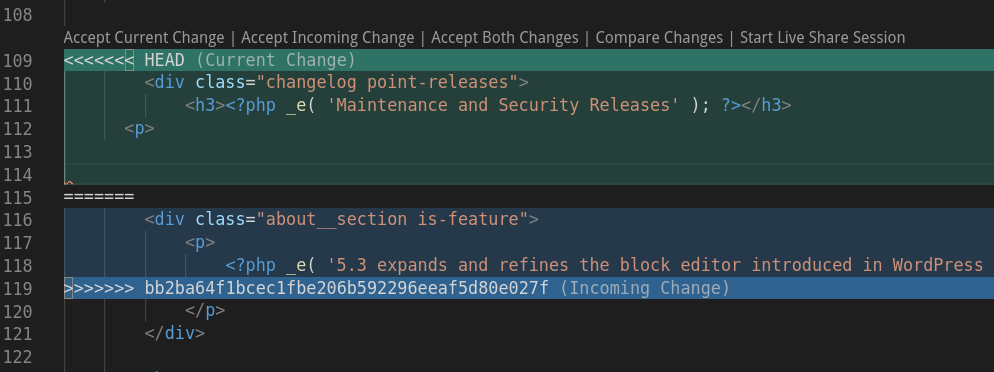
- Open the conflicting file in your text editor or IDE. Note that the conflicting lines are enclosed with
< HEADat the top, and> <commit_id>at the bottom, with=======delineating the two versions. Some IDEs, like Visual Studio Code for example, will highlight the conflicting section:
-
Edit the conflict by choosing one of the two versions of the conflicting line(s), or by editing a version containing both updates.
-
Remove all the delineator notes from the file.
-
Commit and push your changes:
Resolve Conflicts on Drupal Composer-Managed Sites
A content conflict shows in the content-hash section of your composer.lock file. This type of merge conflict happens when two developers install or remove the package(s) in different branches. The branches cannot be merged because the composer.lock file has two different content-hash values.
-
Open the conflicting file in your text editor or IDE. Note that the conflicting lines are enclosed with
< HEADat the top, and> <commit_id>at the bottom, with=======delineating the two versions. -
Edit the conflict by choosing one of the two content-hash values, or by editing a version containing both updates.
-
Remove all the delineator notes from the file.
-
Run the command below:
Resolve Conflicts from Multidevs
Follow the steps below to resolve a merge conflict that is preventing you from merging a Multidev environment.
-
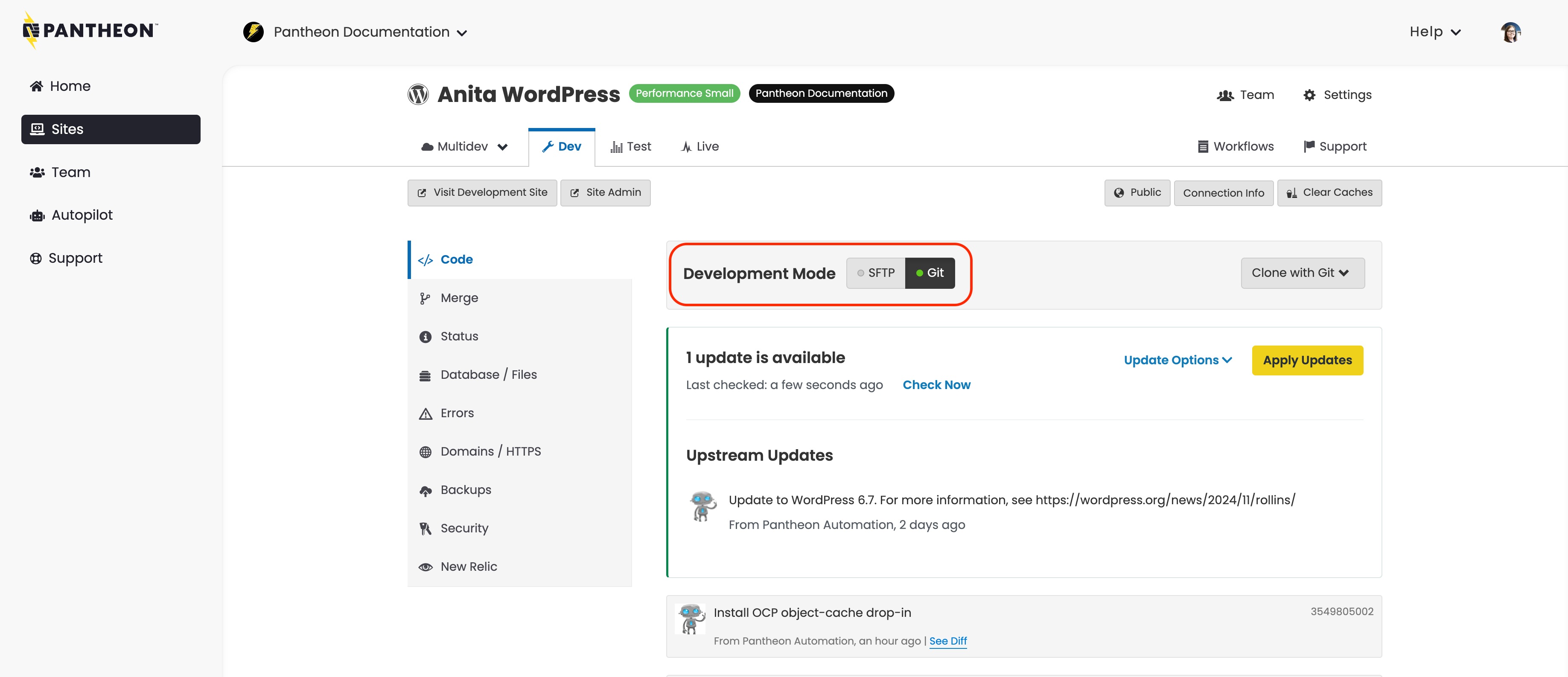
Navigate to your Dev environment > set the Development Mode to Git:
-
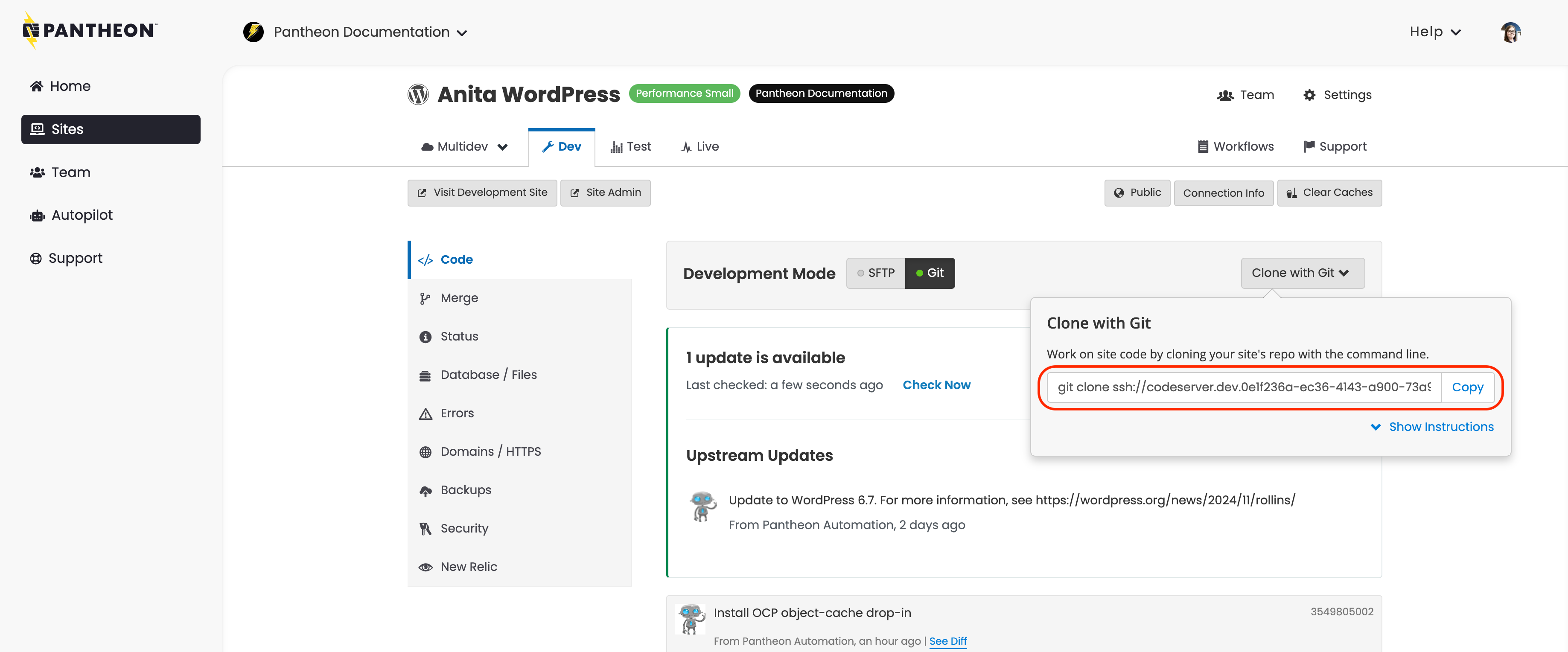
Click Clone with Git to Clone the repository to your local computer:
-
Navigate to the repository directory, change to the
masterbranch and pull the Multidev branch tomaster.-
In the example below, replace
multidevwith the Multidev environment name:
-
-
Resolve the conflicts using the steps above when you receive the Git notification listing the files that are in conflict.