Collaborative Development with an External Repository
Use GitHub to collaborate with the team members on your Pantheon site.
Pantheon provides Git repositories for all sites on the platform. However, some teams might need an external repository hosted by a provider, like GitHub or Bitbucket, to function as the canonical version of the site's codebase. This section shows you how to use Pantheon with an external repository. The example below uses a GitHub account. However, the steps should be similar for any provider.
Git Repositories on Pantheon
The codebase for your site is stored in a Git repository. This includes your versions of Drupal or WordPress core, and all of the custom and contributed modules, plugins, and themes that work together to power your site. It doesn’t include the /sites/default/files/ or /wp-content/uploads/ directories, or your database.
This repository will be a clone of one of the upstreams running on the platform, usually Drupal or WordPress, or one of their forks that our users manage as Custom Upstreams. Your site’s repository on the Pantheon platform will track one of these upstream repositories as a Git remote.
These repositories control the common codebase for several sites. The most common change to an upstream is the release of a new core version. These changes to the upstream repository become available to the sites running them within a day. For individual sites, using GitHub to collaborate on custom code is often a requirement for teams. In order to do so, you’ll need a quick and efficient way to keep your Pantheon repository in sync with GitHub.
The sections below will show you the basics for collaborating with others if your site:
- Is only on Pantheon and you’re moving development to GitHub
- Exists on GitHub and you want to deploy to Pantheon
- Isn’t using Git
- Doesn’t yet exist
Synchronizing Existing Pantheon Sites to GitHub
-
Log in to Pantheon and load the Site Dashboard for the site you want to work on.
-
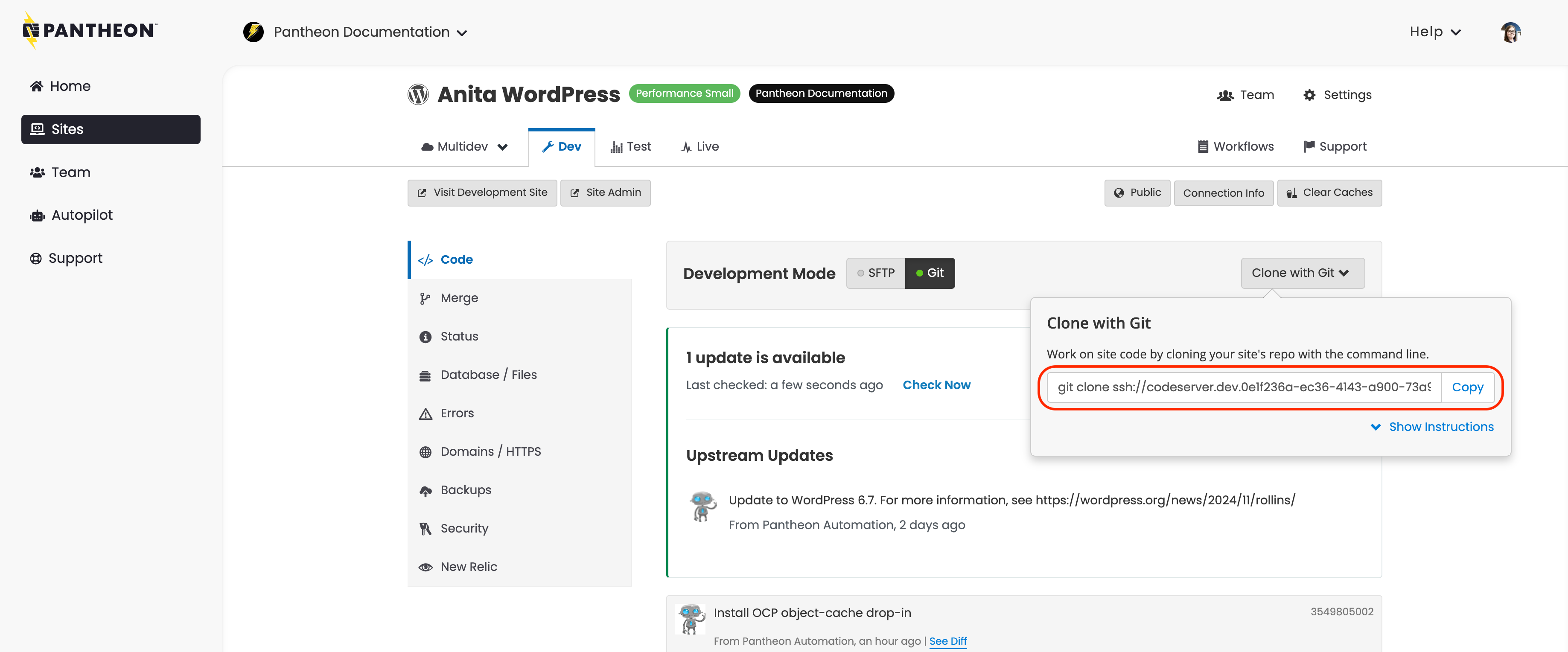
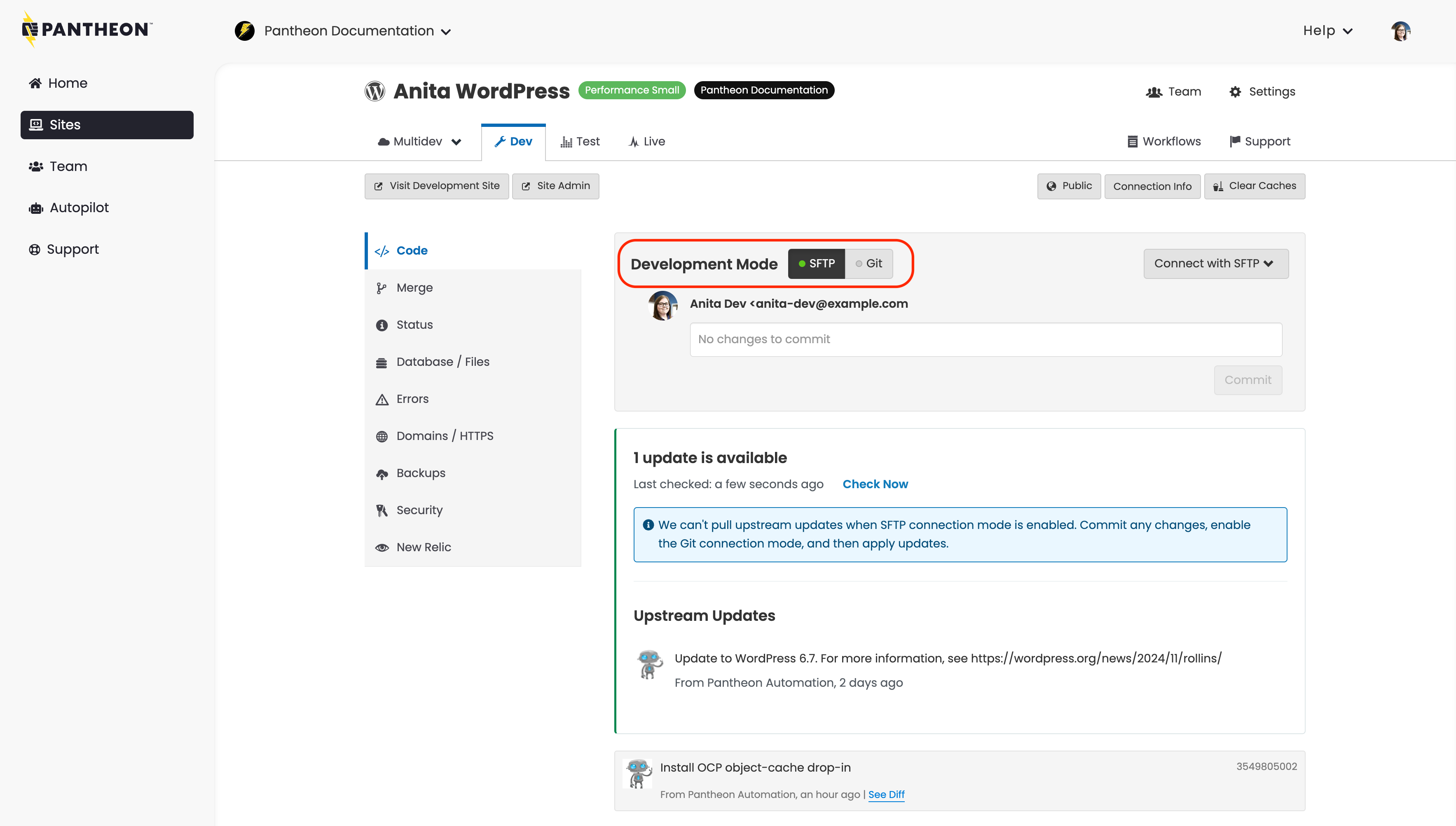
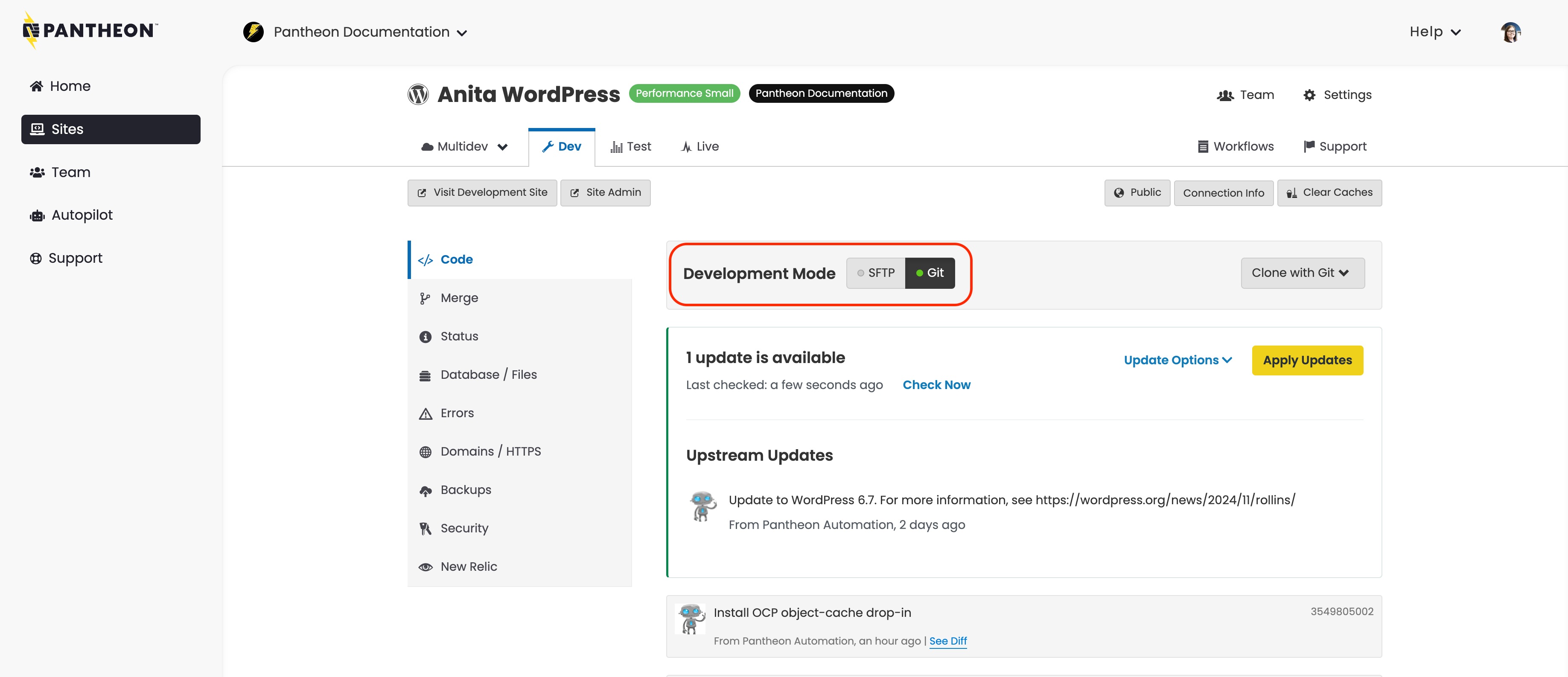
Click the Dev tab, set the Development Mode to Git, and then click Clone with Git:
Your local copy will now track the Pantheon repository as the origin.
-
Change directory into the site repository and verify your connection to the Pantheon server:
The output lists "origin" as the remote with Pantheon SSH Git clone connection information as it's address.
Create a Repository on GitHub
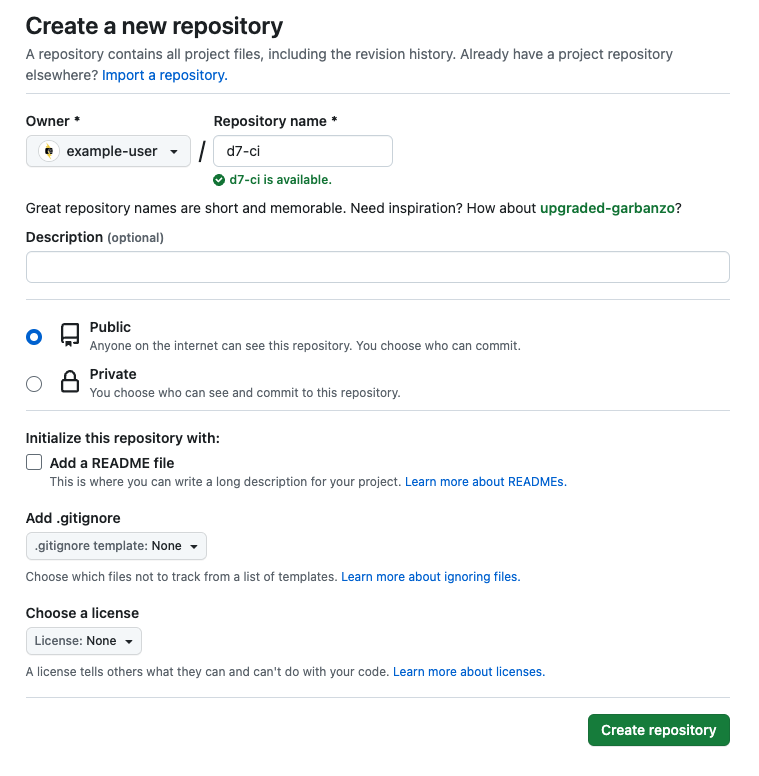
Follow the steps below to configure your GitHub repository.
-
Click the Owner drop-down menu to set the owner to your GitHub user or organization (wherever you want the GitHub repository to live).
- Only members of one or more GitHub organization have the option to change the owner. GitHub users that aren't part of an organization are not given the option to change the owner and will not have an Owner drop-down menu.
-
Enter the Repository name (the examples on this page use d7-ci).
-
Select Public.
-
Keep Initialize this repository with a README unchecked if you want the option to add code to your repository.
-
Select the Add .gitignore checkbox and set the .gitignore template drop-down to none.
-
Select the Choose a license checkbox and set the License drop-down to none.
-
Click Create Repository.
Add the GitHub Repository as a Remote
Replace the word origin with the name you want for your remote to add the GitHub repository as a remote.
- The remote, in this case, cannot be named
originbecause your local clone is already tracking the Pantheon site repository asorigin.
In the example below, the remote is named github.
Configure Origin as a Multi-Remote Destination (Optional)
You can also add another push URL for origin by adding a push URL within .git/config:
Commits will be pushed to both remote destinations automatically on git push origin. Enforce this configuration with all team members when working collaboratively. Thanks to Tom Kirkpatrick for contributing this tip in the Pantheon Community.
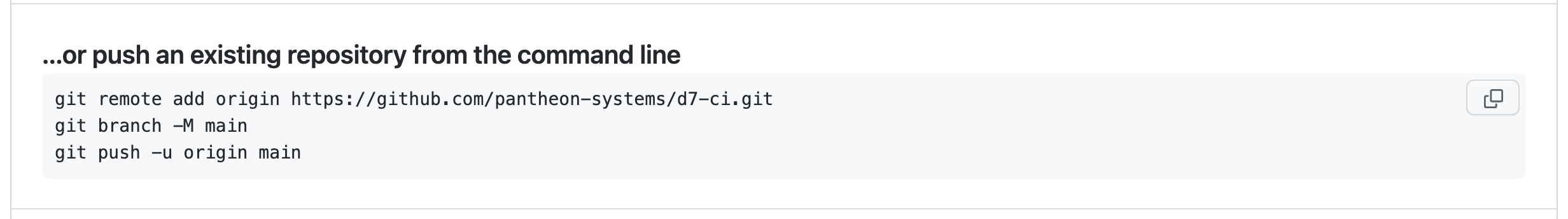
Push the Pantheon Site's Codebase to GitHub
Run the command below in your terminal:
The repository on GitHub now has all of the same code as the existing site.
Migrate Existing Site Repositories to Pantheon
The Pantheon Dashboard provides a guided path for migrating existing sites to the platform. Follow the steps in the Migrate Existing Sites document.
Developing in Sync
You must create the settings.php file to develop in sync.
-
Change directory into
sites/defaultand create the file: -
Add the file to version control and push to both remotes:
-
Push the change to GitHub and Pantheon:
This push to Pantheon failed, because the Development environment was in SFTP mode.
-
Set the Development Mode to Git by clicking on the toggle, or enter the code below in the command line:
-
Push to Pantheon:
The GitHub repository and Pantheon site both now have a
settings.phpfile. This will allow for environment-specific configuration to enable modules through remote Drush calls and other essential functionality.We recommend renaming the remote repository to something more specific than
origin, such aspantheon. -
Rename the remote repository:
Feature Branching
Working with teams on GitHub requires a branching strategy. You must add your colleagues to the site you're developing, both on GitHub and on Pantheon.
Locally, your codebase is in sync with both repositories.
-
Checkout a branch to start working on a new feature:
Since the site is associated with a supporting organization that has a Multidev environment, you can test out any feature. These environments have an 11-character limit for branch names, so you should use short branch names for your feature branches.
-
Download the module and its dependencies in your local environment.
-
Enable the module > test and verify that the module is working.
-
Add, commit, and push to branches on Pantheon and GitHub:
The platform found no Multidev environments associated with the Git branch.
Continue with the steps below to create a Multidev environment.
-
Create a Multidev environment in Terminus:
The module will now be available to activate and test on Pantheon for your colleagues to experience.
-
Add a link to the module's configuration page on the Multidev environment in your GitHub pull request.
Create Pull Request
You are now ready to create a pull request on GitHub. The pull request can include:
-
Links to the Multidev environment where the team can view the effects of the commits
-
@-mentions of team members
-
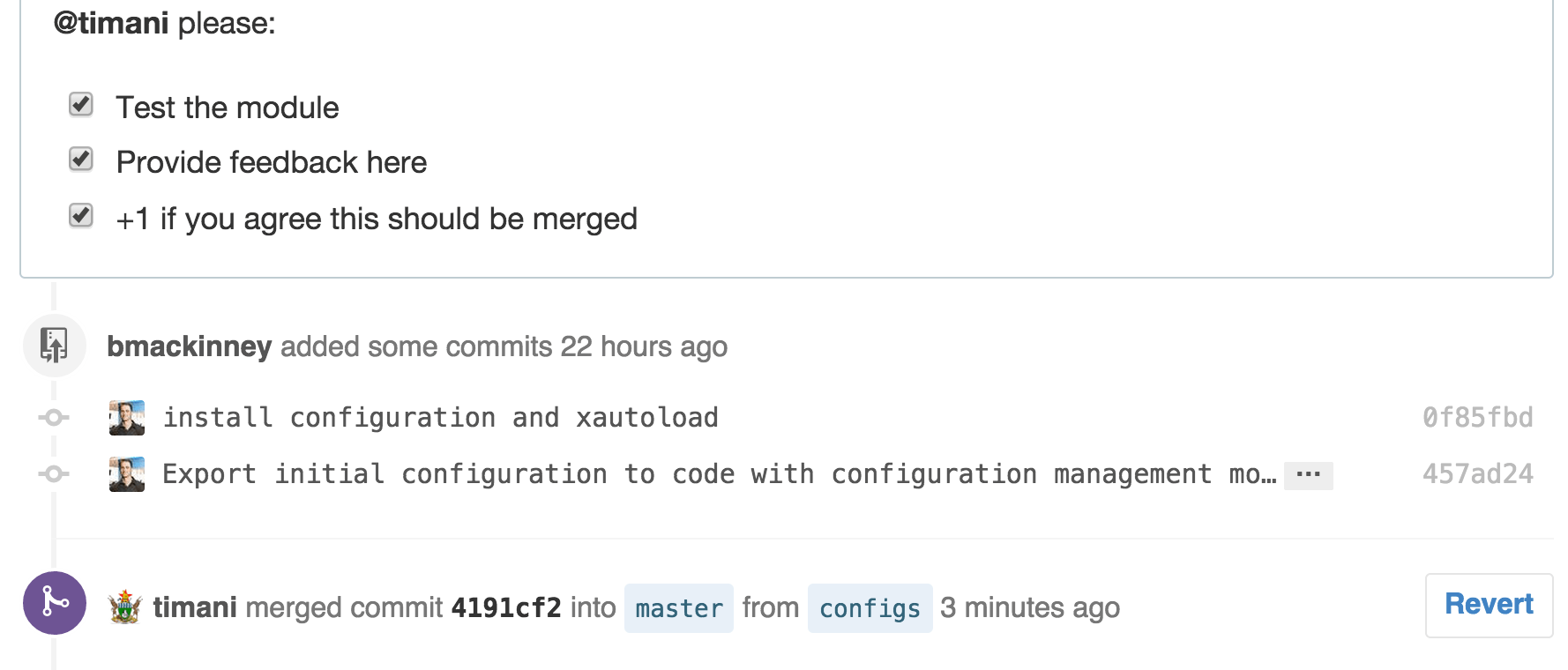
A list of tasks for team members to perform before merging
Timani completed the tasks, we discussed a bit in person, and he merged the PR.
Deploy to Pantheon
-
Checkout the master branch on your local.
-
Pull from github master > push to pantheon master:
Optional Tools to Optimize Workflows
There are other options to further optimize workflows now that you have the basic setup.
-
Pantheon's Build Tools
-
A continuous integration server like Jenkins, Travis CI, Bamboo, or CircleCI
-
A suite of automated acceptance tests using Behat or PHPUnit
These tools allow your team to fully implement continuous delivery with automated testing and continuous integration.